Testing Rigs for construction engineering
Benefit from our experience in manufacturing testing rigs for streets and building constructions.
Benefit from our experience in manufacturing testing rigs for streets and building constructions.
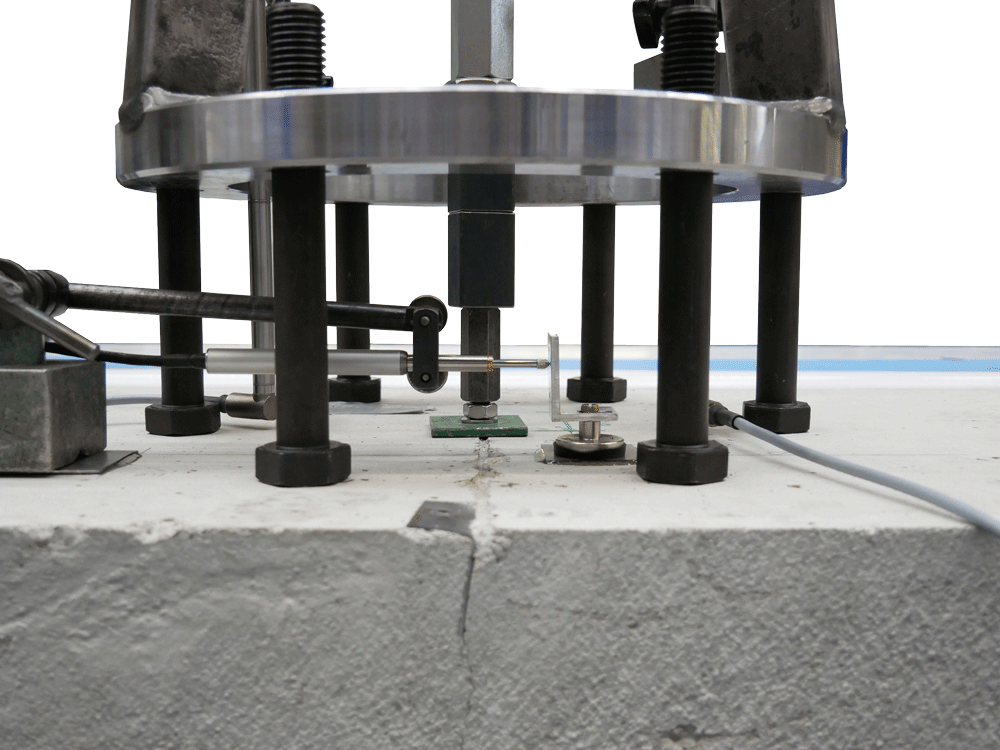
dowel pull-out
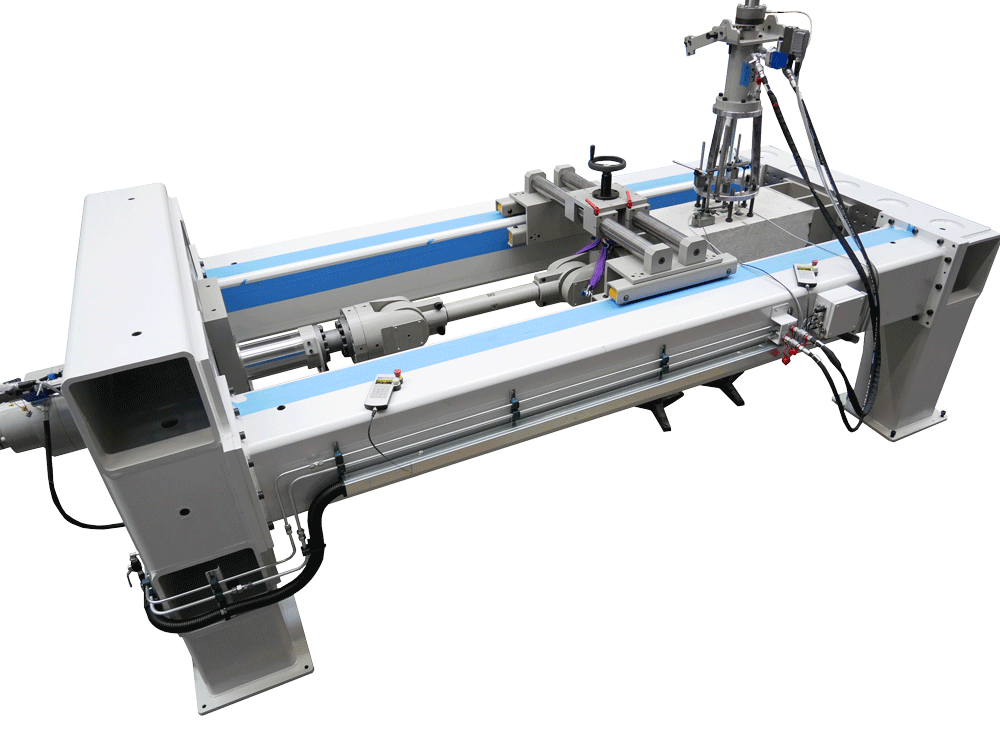
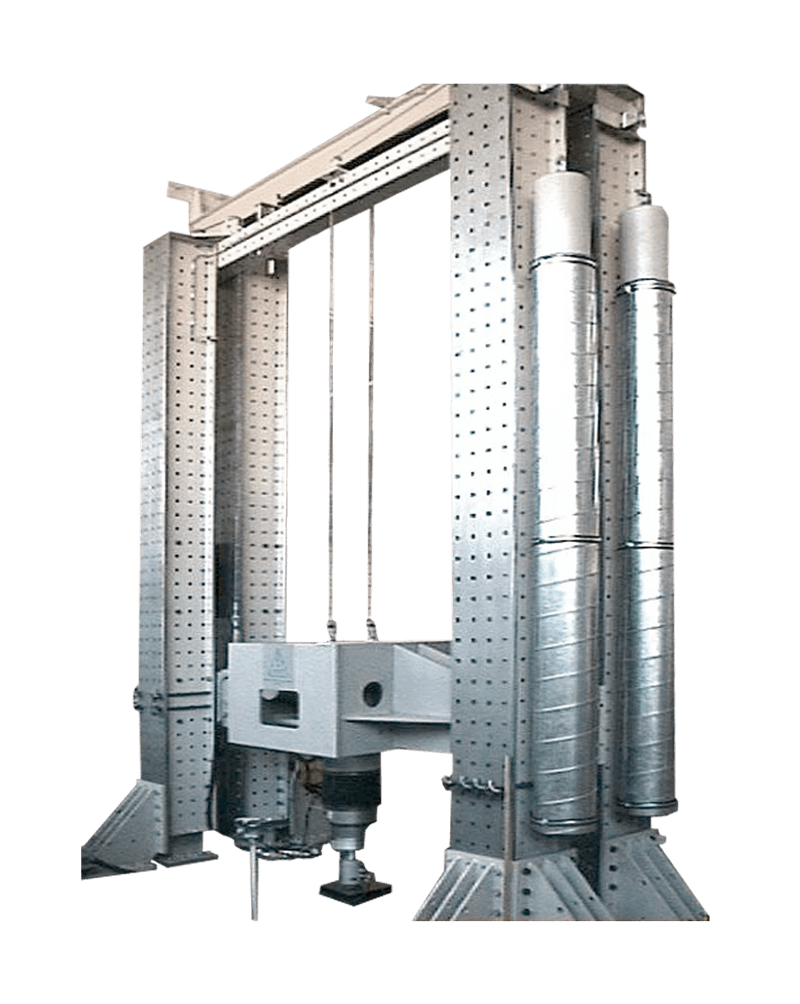
The hydraulic testing machine was designed for cyclic and controlled crack opening at special concrete blocks with reinforcing iron (expanding bodies). At the same time, a constant or gradual pull-out force is applied to a fastener. After the test, the residual load-bearing capacity of the fastener is determined (dowel pull-out).
Changing transverse loads (seismic loads) can be applied to the fastening element using special devices.
Centric pull-out tests can also be carried out on the fastening element and cyclic fatigue stresses can be applied.
The testing machine can also be used for other static and dynamic tensile, compression and bending tests on components and parts or, depending on the requirements, can also be expanded.
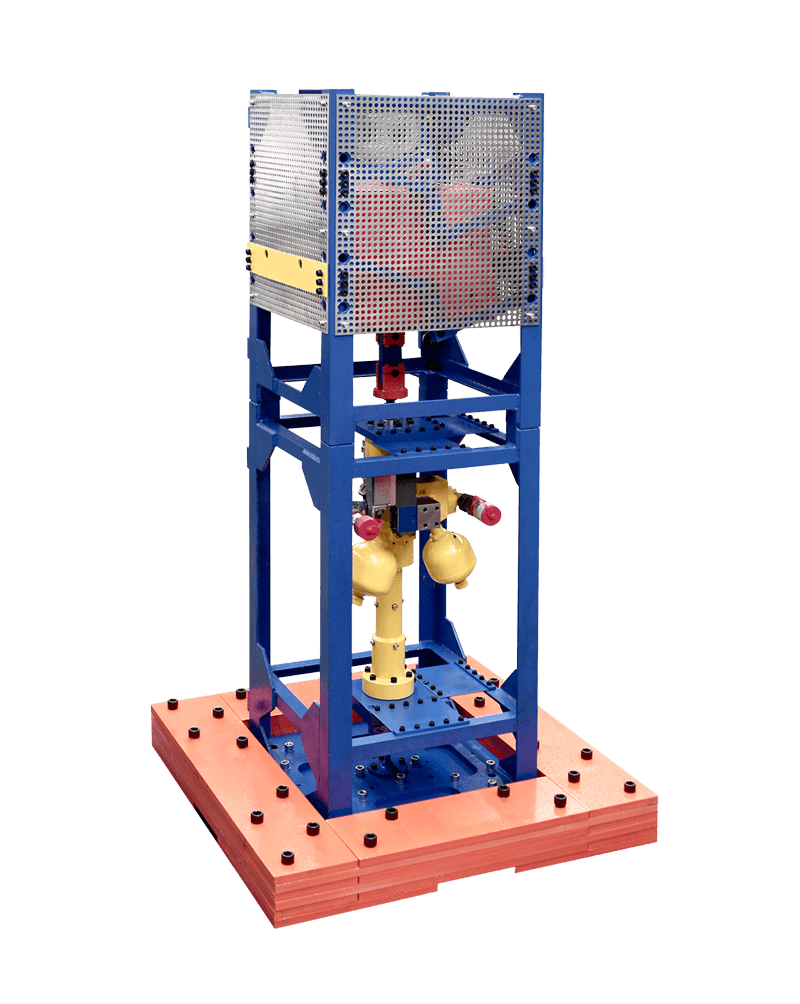
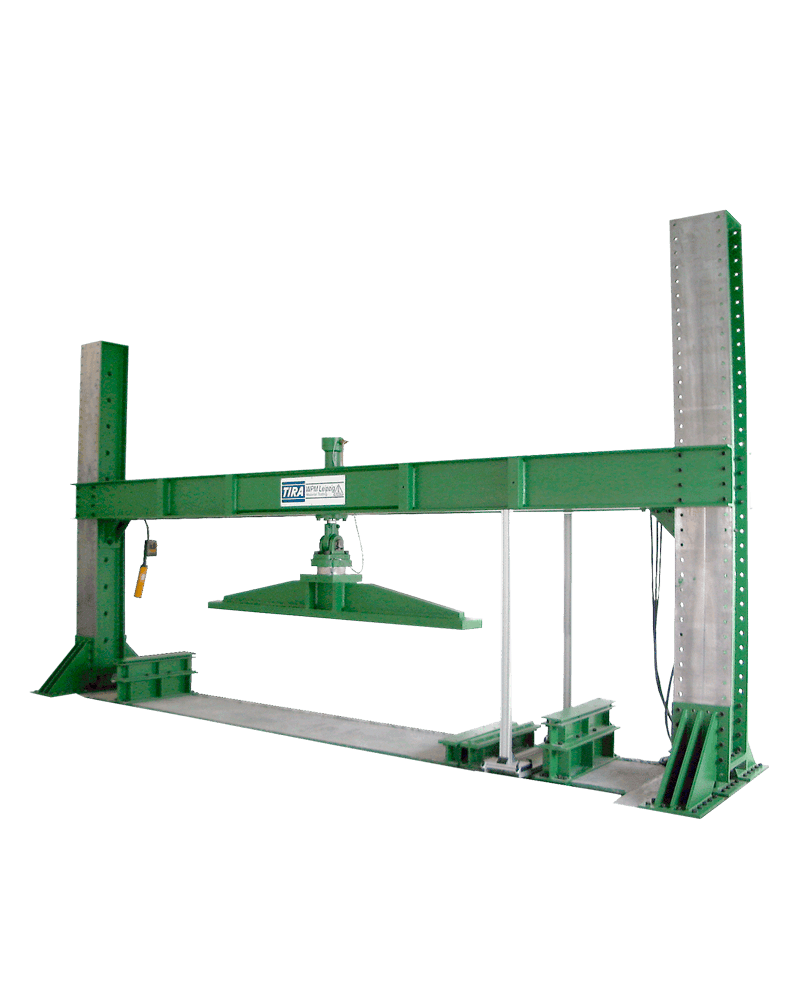
This machine is designed to generate vibrations on buildings and frameworks.
A testing cylinder, connected with the swinging mass without shear forces, generates the necessary amplitude. Due to a special positioning of the swinging mass by an articulated lever system, it is possible to operate the vibration exciter in vertical as well as horizontal position.

This testing rig is used to test beam, ceiling and wall elements according to DIN 1356.
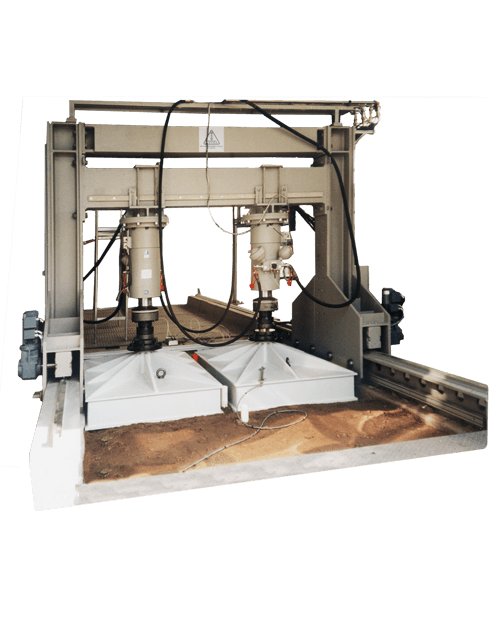
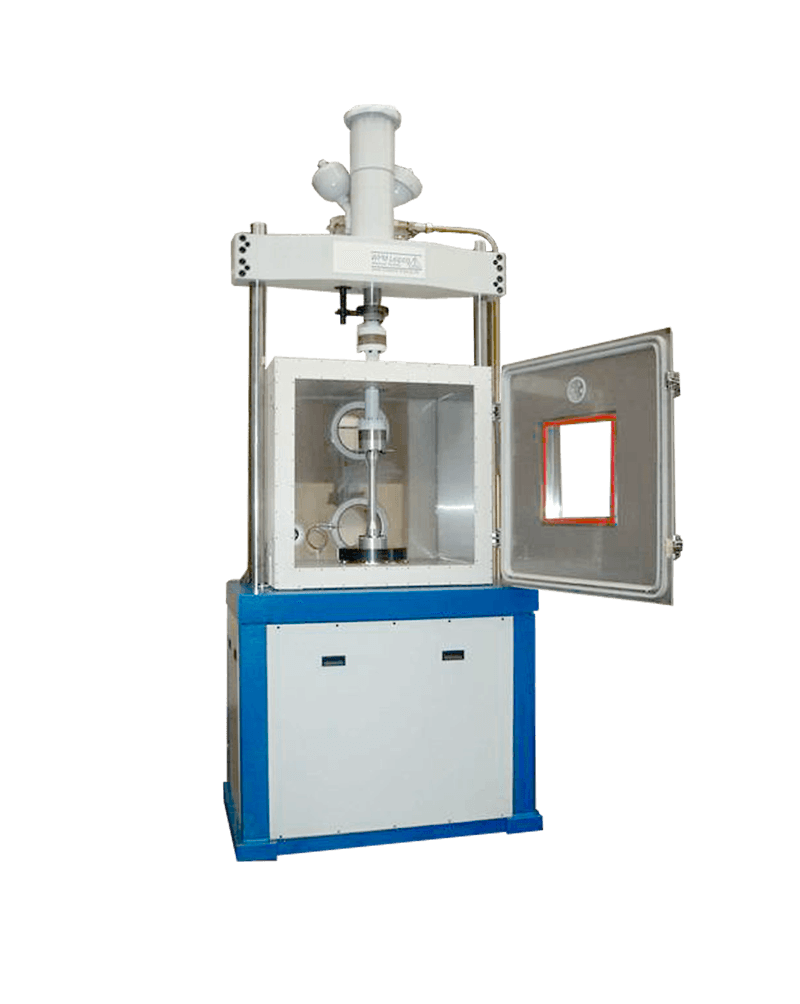
The street and floor testing rig is designed to simulate static and dynamic loads on floor and road. The strength tests are mainly carried out by pressure loads, but static and dynamic compression and tension loads are possible as well.
A load bridge, specially designed for the testing requirements, is driven over one of the two pits to test the floor or road parts on a rail and is positioned in grid spacing.
At the traverse load bridge, testing cylinders are mounted. The testing cylinders hanging downwards can be laterally moved on the traverse on rollers.
The vertex pressure testing machine SDBP 1000 is especially used for testing reinforced concrete beams and tubes.

The testing rig for asphalt is designed to test bituminous or hydraulically bound building material. The specimens are loaded in direction of pressure as well as other derivable testing methods.